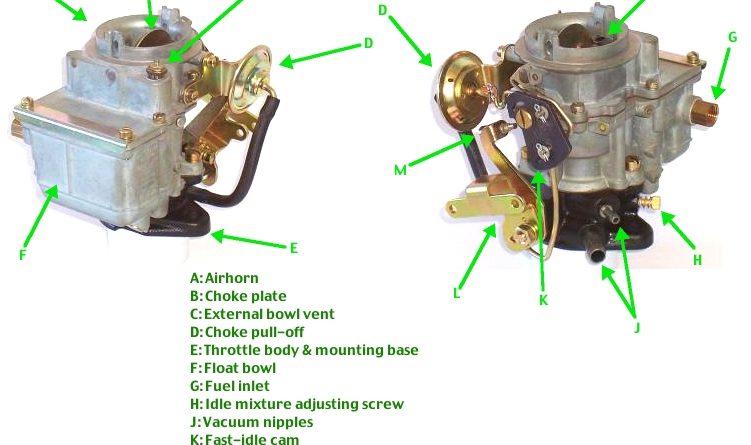
How carbureted engine work?
During 90’s their was a common saying for vehicle’s starting trouble – carburetor mein kachra aa gaya hoga and this was quite true at times. In general, people assumed this to be true for both diesel as well as petrol vehicle but it wasn’t as only petrol engine require mixing of air-fuel before sending the charge to cylinder.
Carburetor was widely used in petrol engines until Multi-point fuel Injection (MPFI) came into market which simplified the process of preparing air fuel mix with increased fuel economy forcing carburetor to disappear from engine bay.
But still we have two wheeler market which rely on carburetor for achieving air-fuel mix as it helps to keep the bike cost at lower side compared to fuel injected bikes. Operation of carburetor is pure mechanical whereas fuel injected system is assisted via. electronic control unit to achieve better control over mix.
Lets understand in detail about carburetor operation –
Overview:
Carburetor is a mechanical device which mixes the air fuel in different amount based on various driving conditions. Depending upon accelerator position, carburetor adjust the ratio of air-fuel mixture before sending to engine cylinder.
Working:
Beneath the venturi, there’s a valve called the ‘throttle valve’. The more throttle open up, the more air flows through the carburetor and the more fuel it drags in from the pipe to the side. With more fuel and air flowing in, the engine releases more energy and makes more power and the vehicle goes faster. This throttle valve is connected through cable or mechanical linkage to vehicle’s accelerator.
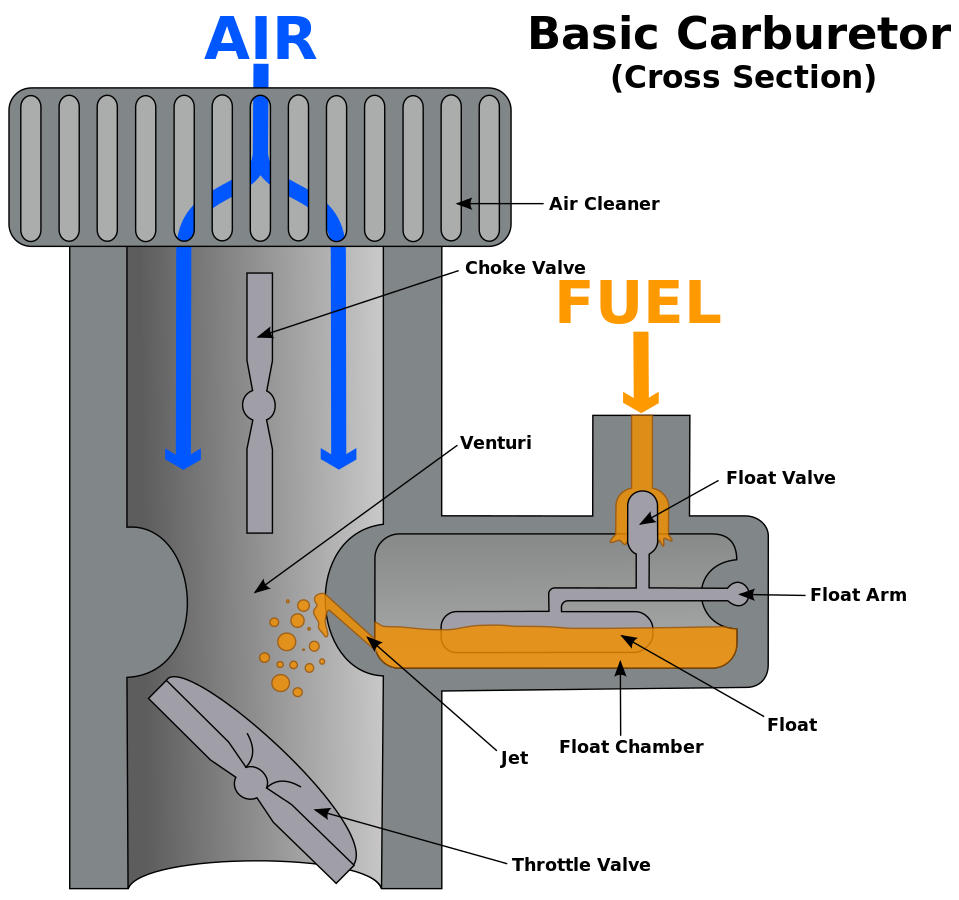 |
| Carburetor Cross Section (Image Source: Wikipedia) |